A. What is Income Tax?
Income Tax is a tax on a person’s income or profit arising from property, practice of profession, or conduct of trade or business.
B. Who are the individuals required to file an Income Tax Return (ITR)?
1. A resident citizen engaged in trade, business, or practice of profession within and without the Philippines.
2. A resident alien, non-resident citizen (OFW), or non-resident alien individual engaged in trade, business, or practice of profession within the Philippines.
3. A trustee of a trust, guardian of a minor, executor/administrator of an estate, or any person acting in any fiduciary capacity for any person, where such trust, estate, minor, or person is engaged in trade or business.
C. Who are the Individuals Not Required to File Income Tax Returns?
The following individuals are not required to file income tax returns:
1. An individual earning purely compensation income whose taxable income does not exceed Two Hundred Fifty Thousand Pesos (P250,000)
2. An individual has only one (1) employer for the taxable year
3. An individual whose income tax has been correctly withheld by his employer,
4. An individual whose sole income has been subjected to final withholding tax.
5. A minimum wage earner.
D. What is BIR Form No. 2316?
The BIR Form 2316, duly stamped “Received” by the BIR, shall be tantamount to the substitute filing of income tax returns by the said employees.
It’s the responsibility of the employer to distribute BIR Form 2316 to employees not later than January 31 after the close of the calendar year for signing.
After the employees signed the BIR Form 2316, the employer will submit this to BIR no later than February 28 after the close of the calendar year.
E. What is the Income Tax Rate for Individuals?
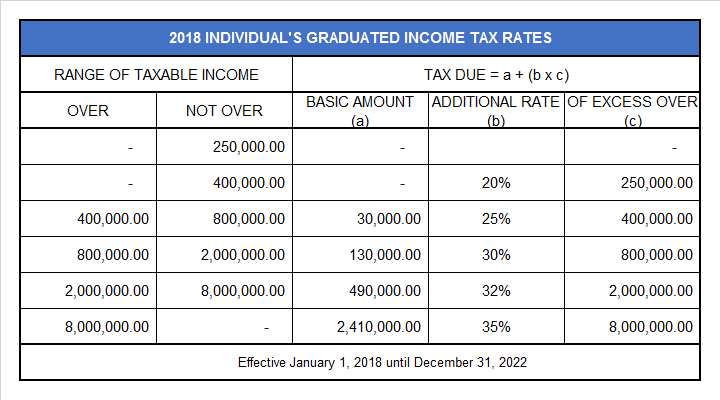
a. For Income earned for taxable years 2018 to 2022, use the 2018 Individual’s Graduated Income Tax Rate Table.
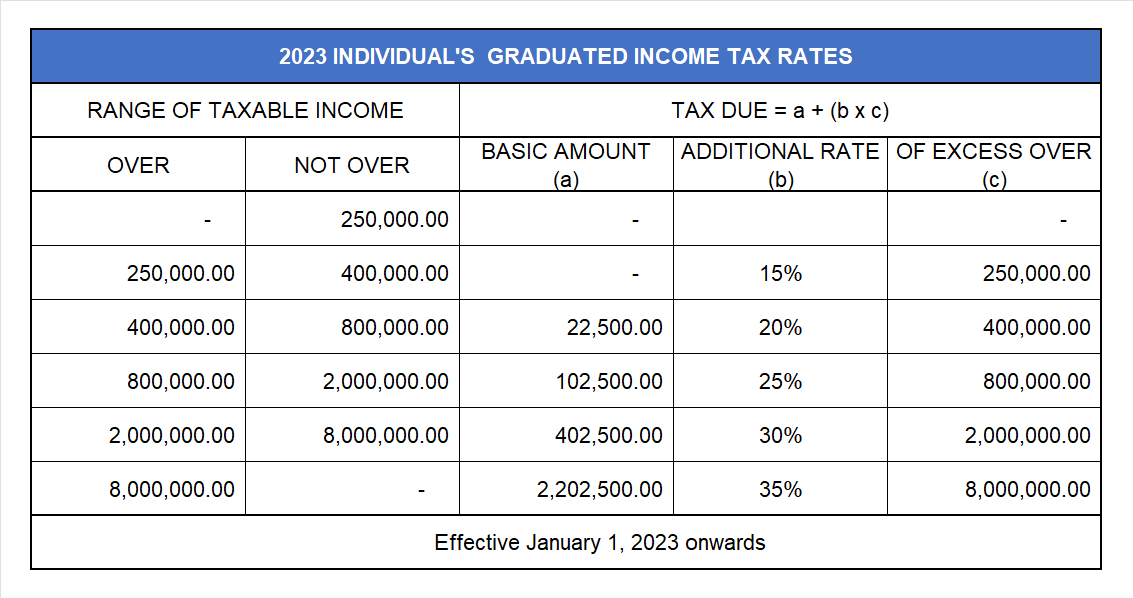
b. For Income Tax earned for taxable years 2023 and onwards, use the 2023 Individual’s Graduated Income Tax Rate Table.
F. How to compute Taxable Income for Compensation Earners?
Taxable Income for Compensation Earners is the Gross Compensation Income minus 13th Month Pay, De Minimis Benefits, and Employee Share in SSS, GSIS, Philhealth, Pag-ibig, and Union Dues.
Compensation income does not need to be reported in the Quarterly Income Tax Return. The same shall be reported in the Annual Income Tax Return only.
G. What is the difference between individuals earning purely from self-employment or practice of profession and mixed-income earners?
For individuals earning purely from self–employment or practice of profession, the eight percent (8%) tax rate is based on gross sales/receipts and other non-operating income in excess of two hundred fifty thousand pesos (P250,000).
For mixed-income earners, the P250,000 reduction is no longer applicable.
H. What is the Income Tax of Minimum Wage Earners?
Minimum wage earners shall be exempt from the payment of income tax on their taxable income. The holiday pay, overtime pay, night shift differential pay and hazard pay received by such earner are likewise exempt.
I. What is Income that is not subject to Income Tax?
The following items shall not be included in gross income and shall be exempt from income taxation:
1. Proceeds of Life Insurance and Amount Received as Return of Premium.
2. Donation and Inheritance.
3. Compensation for Injuries or Sickness
4. Income Exempt under Treaty
5. Retirement Benefits, Pensions, Gratuities, etc.
6. Income derived by Foreign Government
7. Prizes and Awards less than P10,000
8. Prizes and Awards in Sports Competition
9. 13th Month Pay and Other Benefits such as Productivity Bonus not exceeding ninety thousand pesos (P90,000).
10. GSIS, SSS, Medicare, and Other Contributions
11. Gains from Sale of Bonds, Debentures, or other Certificate of Indebtedness with a maturity of more than five (5) years.
12. Gains from Redemption of Shares in Mutual Fund.
J. How to Minimize Income Tax Legally?
If you’re a business owner and/or professional, there are three (3) options you can choose to minimize tax legally.
These are the:
1. Itemized Deduction
2. Optional Standard Deduction (OSD)
3. 8% Income Tax Rate on Gross Sales/Receipts
The taxpayer is required to signify the intention to avail among itemized deductions, optional standard deduction, and 8% income tax rate on the initial quarterly income tax return.
No deductions shall be allowed to individual taxpayers:
1. Earning compensation income under employer-employee relationship and
2. Those who opted to be taxed at an 8% income tax rate on their gross sales and/or receipts.
You can learn more about Itemized Deduction or Optional Standard Deduction (OSD) by clicking here.
K. What is the 8% Income Tax Rate?
Eight Percent 8% Income Tax Rate is an alternative to the Graduated Income Tax Rate.
You will be taxed 8% based on your gross sales/receipts regardless of whether you earn or not.
Another benefit of choosing this is that you will be exempted from filing Percentage Tax.
This is ideal for taxpayers whose:
1. Gross sales/receipt is between One (1) Million to Three (3) Million
2. Who doesn’t have supporting documents for allowable deductible expenses
L. Who is not qualified to avail 8% Income Tax Rate?
1. VAT Registered taxpayer
2. Taxpayers who are subject to Other Percentage Tax
3. Partners in General Professional Partnership (GPP)
4. Barangay Micro Business Enterprises (BMBEs) taxpayers
M. What is included in the Other Percentage Taxes?
1. Domestic Carriers and Keepers of Garages.
2. International air and shipping carriers doing business in the Philippines.
3. Franchises of Gas and Water Utilities.
4. Franchises on radio/TV broadcasting companies whose annual gross receipts do not exceed P10M
5. Oversees dispatch, message, or conversation originating from the Philippines
6. Proprietors, lessees, or operators of cockpits, cabarets, night or day clubs, boxing exhibitions, professional basketball games, jai-alai, and race tracks.
7. Life assurance companies.
8. Agents of foreign insurance companies.
9. Banks, non-bank financial intermediaries, and finance companies.
N. When and Where to File and Pay Income Tax?
Individuals engaged in business/practice of the profession are required to file income tax using BIR Form 1701Q (Quarterly) and BIR Form No. 1701 (Annual) on or before:
1st Quarter – On or Before May 15
2nd Quarter – On or Before Aug. 15
3rd Quarter – On or Before Nov. 15
Annual ITR – On or Before Apr. 15
The return shall be filed through the Electronic Bureau of Internal Revenue Forms (eBIRForms) or Electronic Filing and Payment System (eFPS).
And shall be paid through eFPS or Authorized Agent Bank (AAB) of the Revenue District Office (RDO) where the taxpayer is registered and conducting business.
O. What are the Attachments required in filing your Income Tax?
If your gross annual sales, earnings, receipt, or output exceed Three Million Pesos (P3,000,000) and you choose itemized deduction for your expenses, you need to file:
1. Certificate of Independent CPA duly accredited by the BIR
2. Financial Statements (FS) with Notes to Audited FS that include:
3. Taxes and Licenses
4. Other information prescribed to be disclosed in the notes to FS
5. Statement of Management’s Responsibility (SMR) for Annual Income Tax Return.
If someone withheld tax, you need to attach this to your Income Tax Return:
1. Certificate of Creditable Tax Withheld at Source (BIR Form No. 2307), if applicable.
2. Certificate of Compensation Payment/Tax Withheld (BIR Form No. 2316)
3. Proof of the prior year’s excess credits, if applicable.
4. For amended returns, proof of tax payment and the return previously filed.
5. Summary Alphalist of Withholding Agents of Income Payments Subject to Withholding Tax at Source (SAWT), if applicable.
References:
Republic Act 10963 (Train Law), Revenue Regulations No. 8-2018, Revenue Memorandum Circular 50-2018.
What’s Next?
If you have questions and comments regarding tax, accounting, and business registrations, you can contact us here.